La Ketamine à éteint le cerveau de moutons
2347 vues, 1 réponses
1
A priori ce phénomène n'était pas connu.
Un EEG plat puis un redémarrage sans dégâts.
Dans la série ils ne cherchaient pas mais ils ont trouvé : le k-hole !
"This wasn't just reduced brain activity. After the high dose of ketamine the brains of these sheep completely stopped. We've never seen that before," says neurobiologist Jenny Morton from the University of Cambridge.
"A few minutes later their brains were functioning normally again – it was as though they had just been switched off and on."
https://www.sciencealert.com/ketamine-e … before/amp
Voilà de quoi spéculer sur les effets de la Ketamine et sur son mode d'action.
NDE ? K-hole ? Cette sensation de reset a déjà été décrite par des ketausaures.
Effectivement, il y a matière penser que cette forme de mort cérébrale temporaire n'y est pas étrangère.
At the highest intravenous dose used (24 mg/kg), in 5/6 sheep we observed a novel effect of ketamine, namely the complete cessation of cortical EEG activity. This persisted for up to several minutes, after which cortical activity resumed. This phenomenon is likely to explain the ‘k-hole’, a state of oblivion likened to a near death experience that is keenly sought by ketamine abusers.
3 étapes identifiées :
Characteristic dose-dependent behavioural and quantitative EEG responses of sheep to ketamine
The behavioural response of sheep to ketamine can be separated into three distinct sequential phases based on the behaviour and the electromyogram (EMG)/electroocculogram (EOG) activity (Fig. 1). The first phase, seen shortly after delivery of ketamine, is characteristic of the well-described anaesthetic effect21. During this phase, voluntary movement is suppressed, as are eye movements, although the eyes remain open and they have intact palpebral (eye blink) reflexes. In this phase there is typically increased muscle tone22, which was evident in the EMG trace (see below). In the second phase, sheep are conscious and respond to gentle sensory stimulation such as incidental noise or movements in the visual field, but do not engage in voluntary movement. This corresponds to the dissociative analgesic phase. During the third phase, sheep are conscious and appear alert, with awake levels of EMG and EOG activity, although again they do not engage in voluntary movement. The duration of each of these phases is dose-dependent (data not shown).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-66023-8
Dernière modification par Mister No (17 juin 2020 à 18:35)
Just say no prohibition !
Hors ligne
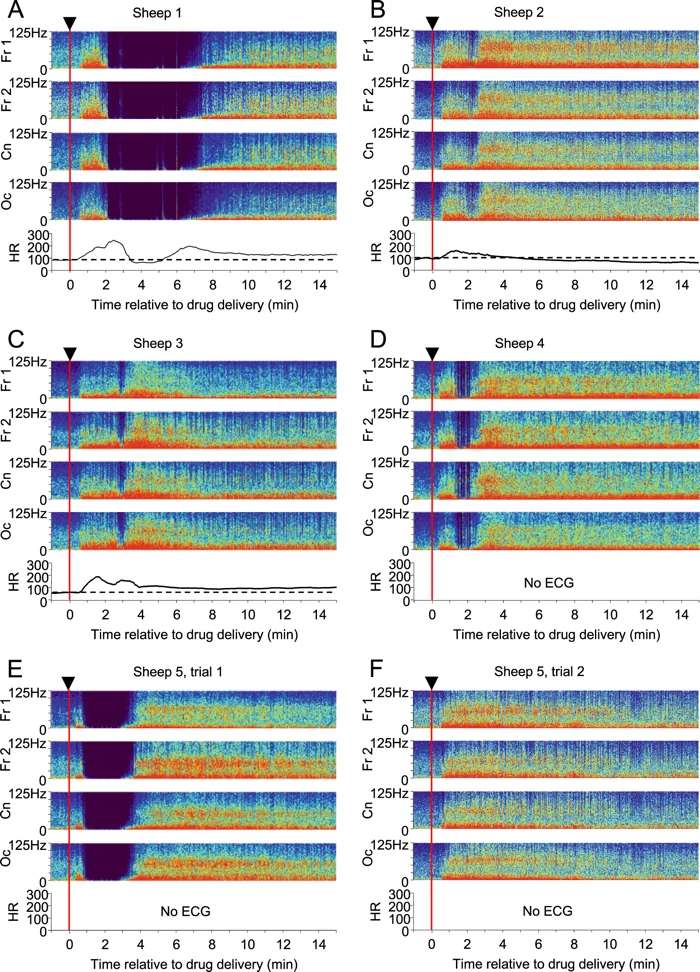
Sympa les EEG ! Les résultats sont déroutants , je me demande si cela n'explique pas pourquoi mes trips "k holes" de kétamine sont si "différents". Genre cela ne ressemble pas du tout au LSD ...aux champignons... Et d'ailleurs en Sniff ça ne ressemble pas beaucoup à l'intraveineuse de kétamine je trouve.
Oui mes hallucinations (et les hallucinoses quand je réatterris) sont particulièrement spectaculaire, étrange, mystique. Si l'étude et ses conclusions se révèlent exactes, alors j'imagine que l'arrêt de certaines fonctions cérébrales doit énormément influencer le trip. Vu les dosages (3-24mg/kg) il y a de quoi faire de jolis k holes. Je me demande si cette découverte ne permet pas d'expliquer POURQUOI MES HALLUCINATIONS SONT TELLEMENT DIFFERENTES AVEC CETTE SUBSTANCE ?
Et aussi c'est une substance que j'ai vraiment poussé dans les dosages et sans prendre le risque de mourir d'une surdose car même si je m'envoyais des bonnes doses (100-150mg env) en IV cela ne suffisait pas pour me menacer. C'est d'ailleurs l'une des propriété de la kétamine : ses faibles risques pour les OD face aux autres médicaments de la même catégorie. Après c'était moi et je connais mes limites, je déconseil évidemment à ceux qui me lisent de faire ce que j'ai fait et prendre les mêmes risques que moi (à savoir pratiquer ivd kétamine seul).
Aussi il faut que le trip soit agréable et cela n'est pas du tout évident. Cela m'arrive mensuellement "quoi?! les kholes ça t'es agréable!? mais c'est censé être négatif , une sorte de bad trip, les kholes , non?" Ben moi je répond que c'est ce que je préfère. et que quand je reviens d'un khole et que je reprends conscience, que je remonte à la surface dans mon lit. Que je commence à réapercevoir la forme des membres de ma chambre etc. Avec le plafond qui glisse, les couleurs monochromés , tout est étrange etc. Ben quand cela m'arrive je suis déçus, car je comprends que le trip est derrière et non pas devant ^^. Son effet anxiolytique me permet aussi de ne pas bad trip face aux hallucinations qui remettent vraiment en question le réel, car certaines visions sont absurdes, des complexités insolubles, boucles, tourbillons de tourments et de visions sublimes. Des beautés générés à une vitesse grandiose. Des choses semblent secrètent, interdites, précieuses et on ne peut pas les ramener, elles restent là bas, inaccessible. D'ailleurs j'ai souvent l'impression que mon cerveau du quotidien et son esprit, fonctionne au ralenti, à faible capacité; Alors que dans l'autre monde du k hole, là il est surpuissant : je peux créer des terres, mers, vents, animaux, sons , lumières, humidité etc en quelques fractions de secondes puis animer le tout etc. Alors qu'au quotidien, j'ai déjà du mal à rester concentré sur la route..
C'est de l'horreur cosmique, Chtulu est prêt à franchir un trou de ver pour franchir l'espace temps et balancer des météorites sur vous. J'adore les trips de kétamine en IV vers 100-150mg en fonction de la tolérance, seul avec de la musique/vidéo/cinéma en fond. Même si je me rappel que peu de chose dans mes trips
Dernière modification par Rick (18 juin 2020 à 07:13)
Hors ligne
Sujets similaires dans les forums, psychowiki et QuizzZ
 |
[ Forum ] Les effets du cannabis sur le cerveau
|
12 |
 |
[ Forum ] La cocaïne et votre cerveau
|
3 |
 |
[ Forum ] Etude - La zone du bonheur localisée dans le cerveau
|
19 |
 |
[ PsychoWIKI ] Kétamine, effets, risques, témoignages |

 20
20 0
0 0
0
 Soutenez PsychoACTIF
Soutenez PsychoACTIF